The strategy of finfish
culture founding in Chile
(Revised version of April 28, 2012)
Masatoshi
FUTAGAWA
August 9, 2017
Exportation of salmons and trout reduced
to 513 thousand tons (-13%) and 3.8 billion USD (+8%) in 2016
compare to 2015 due to influence of toxic algae bloom. Also, natural resource of coastal fishes are decreasing
much due to overfishing, and affect costal life which happening in all over the
world. Thus, it needs alternatives culture species of salmons to minimize risk
of the business and recover resource of costal fishes to improve costal life. The
keywords are “Economical sustainability”, “Minimum influence for nature” and
“Less energy consumption”.
1.
Conditions
1.1. Fish
characters
Ideal
habits for commercial culture are bellow.
- · Easy to produce juvenile
- · Grow fast; grow to marketable size in a minimum time
- · Wide tolerance of water change about WT, pH, DO, turbidity, ammonia and other chemical contaminations
- · Low protein requirement, herbivorous or omnivorous are ideal, which reduce feeds cost
- · High feeds conversion rate
- · Resist to parasites, bacteria, fungi and virus
1.2. Market
Basically the fish has high value and volume of demand at market.
There are two markets, international and local market, and requirements are
follows.
International market
The fish
competitive in world markets it should large volume to enough to fill container,
constant supply, standardized size and quality, safe (no contamination) and traceable
about production history regarding feeds, usage of chemical and medicine. Particularly,
the meet color white except tuna, the name commonly known widely and the price is
reasonable of cause.
Local market
The
market requires seasonal diversity and reasonable price than high volume. Chilean
soul fish, commonly knows fish, and high price such as flatfish “Lenguado”,
Mulata, Cusk-eel “Congrio”, Yellowtail amberjack “Dorado”
2.
Culture methods
There are three culture
methods as below and it is important to coordinate with those methods, fish behavior
and available area condition.
2.1. Cage culture
Cage culture is ideal for
mass production like salmon production to take advantage of no need water system.
Chile has advantages for this method as availability of culture know-how and
skilled workers from salmon industry, availability of local fish meal or fresh
fish, less contamination water and steep depth close to coast. Disadvantages
are seasonal high wave and poaching by human and sea wolf. High wave problem
can be solves to rearing off-shore (not much far in Chile due to steep bottom),
using submersible cage and security system minimize poaching.
2.2. Land base culture
Chile has available huge land
space where not suitable to people live. The area utilize for land base culture
with earthen pond covered by liner and roofing with plastic or RAS (Recircular
Aquaculture System). This method is more secure and controllable than sea cage.
However, it requires high initial and running cost for electric and maintenance.
Also, the method requires sophisticate technology and skilled worker. Thus, the
method is targeted to high value fish with high productivity. Additionally, we
should be careful to not fall in trap such as repeat medical treatment for disease
(parasite, bacterial and virus) due to high density culture.
2.3. Releasing juvenile (Marine ranching)
The activity consist seed
production by SISP (Semi Intensive Seed production method), artificial reef
installation, releasing juvenile and management at open sea. This method is ideal
to meets all key words that maintain marine resource sustainably and care
costal life. In fact, the activity operated more than 50 years in Japan and it
shows some natural resources are recovered. The method requires high quality
and low cost juvenile and well recovers of products. Therefore, SISP produce high
quality and low cost juvenile, artificial reef protect released juvenile from
predator and fishing sustainably based on biological sampling at releasing area.
Furthermore, artificial reef increase productivity that not only released fish
but also aggregated wild fish and form ecosystem.
3.
Strategy
Most important point is the
make vision of fish culture after 10 years and make combination of culture
methods and candidate fish, projection with time table. Then concentrate force,
fond and manpower, from industrial and academic, coordinate results from some
sectors and revise a plan after evaluation every year.
Additionally, investor has
not much interest to aquaculture due to the aquaculture needs too much time
(years) to take permissions and available area are limited because of low. For
the development of aquaculture, it should the permit shorter and simply even
give an advantage to investors. Possibly, government authorizes special permission
at particular area. New activity needs new regulation.
4.
Tactics
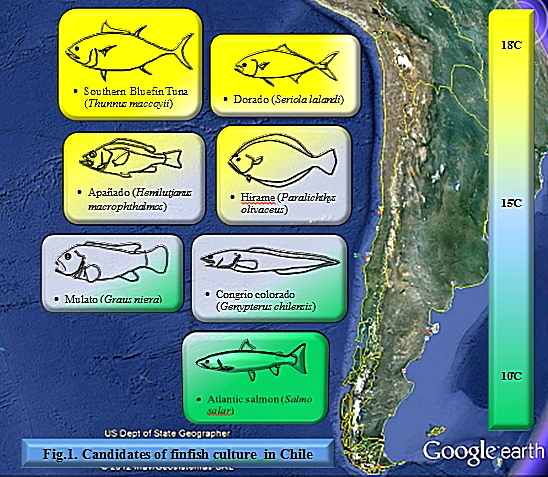
4.1. Candidates
Culture species selection is very important
to minimize risk when environmental change (El niño) or disease prevalent (ISAV). Requirements of culture species are
market size, price, production cost and ease of production, market size. Also
consider to wide water temperature range, from warm water to cold water (north
to south) and make some combination. Candidates show bellow.
- · Southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii); Very high price (28USD/Kg), high demand in world market, available at off-Iquique (need survey). Very difficult to produce juvenile but tuna grow-out culture is existing at Japan, Australia and Mexico, ideal WT is around 20 ̊C. Growth very fast (16Kg within 2 years) but require huge feeds. It requires fusibility study about availability of broodstock.
- · Yellowtail amberjack “Dorado” (Seriola lalandi); High price (10USD/Kg), high demand in world market, habit middle to northern part. Artificial seeds are available locally. Ideal WT is 18 ̊C above. Grow fast (3Kg within 2 years) and take feeds much. The fish require high oxygen water and parasite control in high density culture.
- · Japanese flounder “Hirame” (Paralichthys olivaceus); High demand, high price (15USD/Kg), exotic species. The technologies from seed production to grow-out are available. Ideal WT is 18 ̊C above and grow normal (1.2Kg within 2 years). Produce high quality product to compete low quality cheap products from Korea. Another option, produce native flounder after solve slow growth and high temper problems by selection technic.
- · Grape-eye seabass “Apañado” (Hemilutjanus macrophthalmos); Indigenizes species in Peru and Chile. Possibly, high demand, good price. Habit northern rocky coast. Probably not difficult seed production. Ideal WT is 16 ̊C above and grow normal.
- · Red cusk-eel “Congrio colorado” (Genypterus chilensis); High demand in world market, kind of Kingklip, good price. Habit southern rocky coast. Probably not difficult seed production. Ideal WT is 16 ̊C and grow normal.
- · Black wrasse “Mulata” (Graus nigra); Indigenizes species in Chile. High demand in national, good price. Probably not difficult seed production. Ideal WT is 16 ̊C and grow normal.
4.2. Methods
Cage poly-culture and Marine ranching
Intensive culture gives high stress to fish
and fish reduces immunization then it trigger to disease infection (parasite, bacteria
and virus). Intensive method has no sustainability which evidence of salmon
culture, prawn culture history. Therefore, recommend compound culture such as
combination of cage culture, medium density poly-culture, and Marine ranching.
This idea comes from IMTA
(Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture) which project operated Canada,
UK, EU counties, Israel, Chile and China. The concept that waste from cage culture utilize to shellfish and macroalga in
order to minimize environmental contamination and enhance productivity.
Culturing Dorado (8 Kg/m3) and
San pedro (Pacific beakfish, Oplegnathus
insignis, 100 ind./cage) which cleaning cage (20x20x20m). Shelters are
installed under the cages and release Congrio, Mulata and Apañado juvenile. The excess feeds and feces
from cage are fall down to shelters and grow those fish and minimize bottom
contamination.
4.3. Land base flounder culture with
macroalga culture
Hirame land base culture operates with RAS (Recirular Aquaculture system) to increase WT and growth. Drain water path to macroalga and mollusks culture tank,
remove organic matter and chemical, and minimize contamination for environment.
This concept is similar to IMTA which culture with flounder, scallop and seaweed.





Comments
Post a Comment